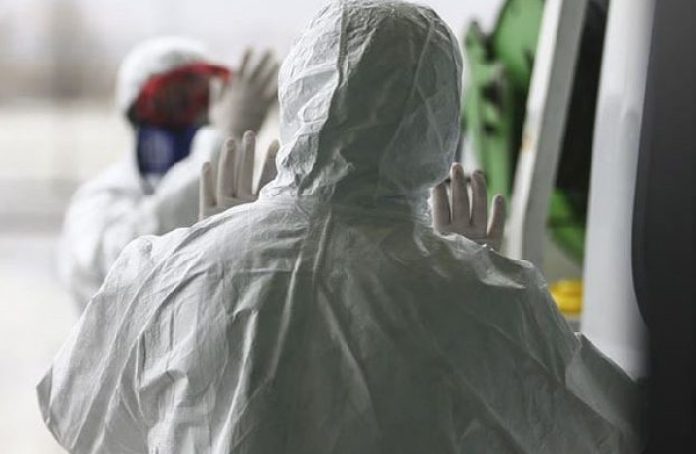
The World Health Organization (WHO) today (July 23) warned of the threat posed by COVID-19 to health workers across Africa.
More than 10 000 health workers in the 40 countries which have reported on such infections have been infected with COVID-19 so far, a sign of the challenges medical staff on the frontlines of the outbreak face.
This comes as COVID-19 cases in Africa appear to be gathering pace. There are now more than 750,000 cases of COVID-19, with over 15,000 deaths. Some countries are approaching a critical number of infections that can place stress on health systems. South Africa is now among the worst-hit countries in the world.
“The growth we are seeing in COVID-19 cases in Africa is placing an ever-greater strain on health services across the continent,” said Dr Matshidiso Moeti, WHO Regional Director for Africa. “This has very real consequences for the individuals who work in them, and there is no more sobering example of this than the rising number of health worker infections.”
So far, about 10% of all cases globally are among health workers, though there is a wide range between individual countries. In Africa, information on health worker infections is still limited, but preliminary data finds that they make up more than 5% of cases in 14 countries in sub-Saharan Africa alone, and in four of these, health workers make up more than 10% of all infections.
Inadequate access to personal protective equipment or weak infection prevention and control measures raise the risk of health worker infection. Surging global demand for protective equipment as well as global restrictions on travel have triggered supply shortages.
Health workers can also be exposed to patients who do not show signs of the disease and are in the health facilities for a range of other services.
Risks may also arise when health personnel are repurposed for COVID-19 response without adequate briefing, or because of heavy workloads which result in fatigue, burnout and possibly not fully applying the standard operating procedures.
In many African countries, infection prevention and control measures aimed at preventing infections in health facilities are still not fully implemented.
When WHO assessed clinics and hospitals across the continent for these measures, only 16% of the nearly 30 000 facilities surveyed had assessment scores above 75%.
Many health centres were found to lack the infrastructure necessary to implement key infection prevention measures or to prevent overcrowding. Only 7.8% (2213) had isolation capacities and just a third could triage patients.
“One infection among health workers is one too many,” said Dr Moeti. “Doctors, nurses and other health professionals are our mothers, brothers and sisters. They are helping to save lives endangered by COVID-19. We must make sure that they have the equipment, skills and information they need to keep themselves, their patients and colleagues safe.”
WHO has been working closely with health ministries to reduce health worker infections since the outbreak began. The Organisation has trained more than 50 000 health workers in Africa in infection prevention and control, with plans to train over 200 000 more, as well as providing guidance documents and guidelines on best care practices and the most up-to-date treatment regimes.
WHO is also helping to fill gaps in the supply of personal protective equipment. Currently, 41 million items of personal protective equipment are ready to ship from China to cover the needs of 47 African countries. Shipments for an initial set of 23 African countries are planned to start during this weekend.
As a result of concerted efforts by WHO and partners some African countries have managed to reduce health worker infections considerably. For example, two months ago over 16% of COVID-19 infections in Sierra Leone were among health workers.
The figure has now dropped to 9%. Cote d’Ivoire has reduced the proportion of infections among health workers from 6.1% to 1.4%. Scaling up infection prevention and control measures can further reduce infections among health workers.